Structural, Optical and Electronic Properties of Perovskite and Boron Nitride for Solar Cell Application
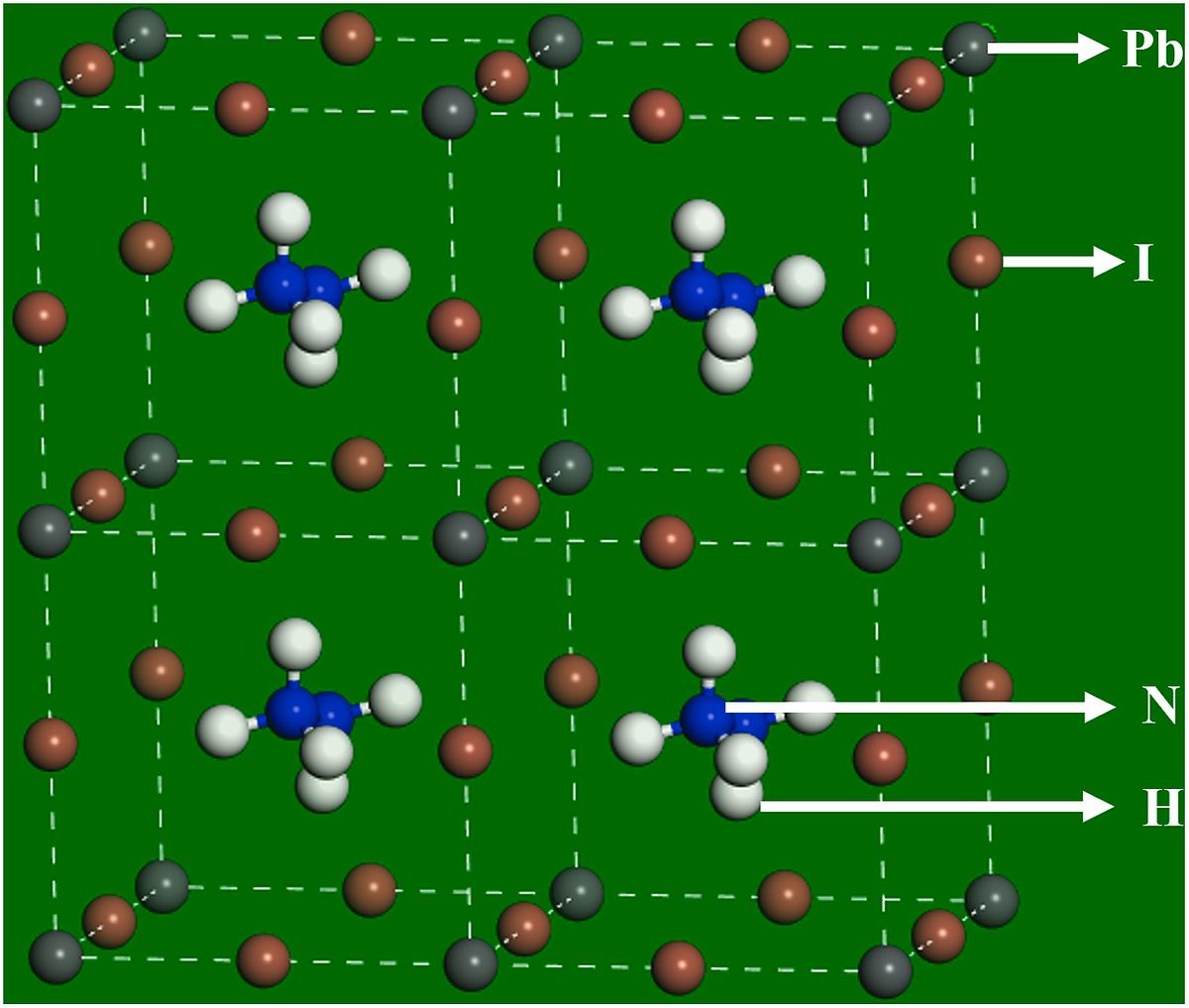
The most commonly researched organic perovskite is CH3NH3PbI3 (MAPI) containing methylammonium (MA, CH3NH3+) ion in the A site of ionic radius 2.17 Å resulting in a tolerance factor of 0.9. Hydrazinium ion (HA, N2H5+), a candidate for A site cation, has a similar ionic radius to that of MA, leading to a tolerance factor of 0.92 for hydrazinium lead iodide (HAPI) perovskites. Hence, HAPI is a stable structure and alternative to MAPI perovskite in optoelectronic (OE) research. HAPI has a higher absorption coefficient in the visible wavelength region with an optimal band gap which can demonstrate a remarkable improvement in solar cell performance.
Publication: Exchange-correlation functional's impact on structural, electronic, and optical properties of (N2H5)PbI3 perovskite

