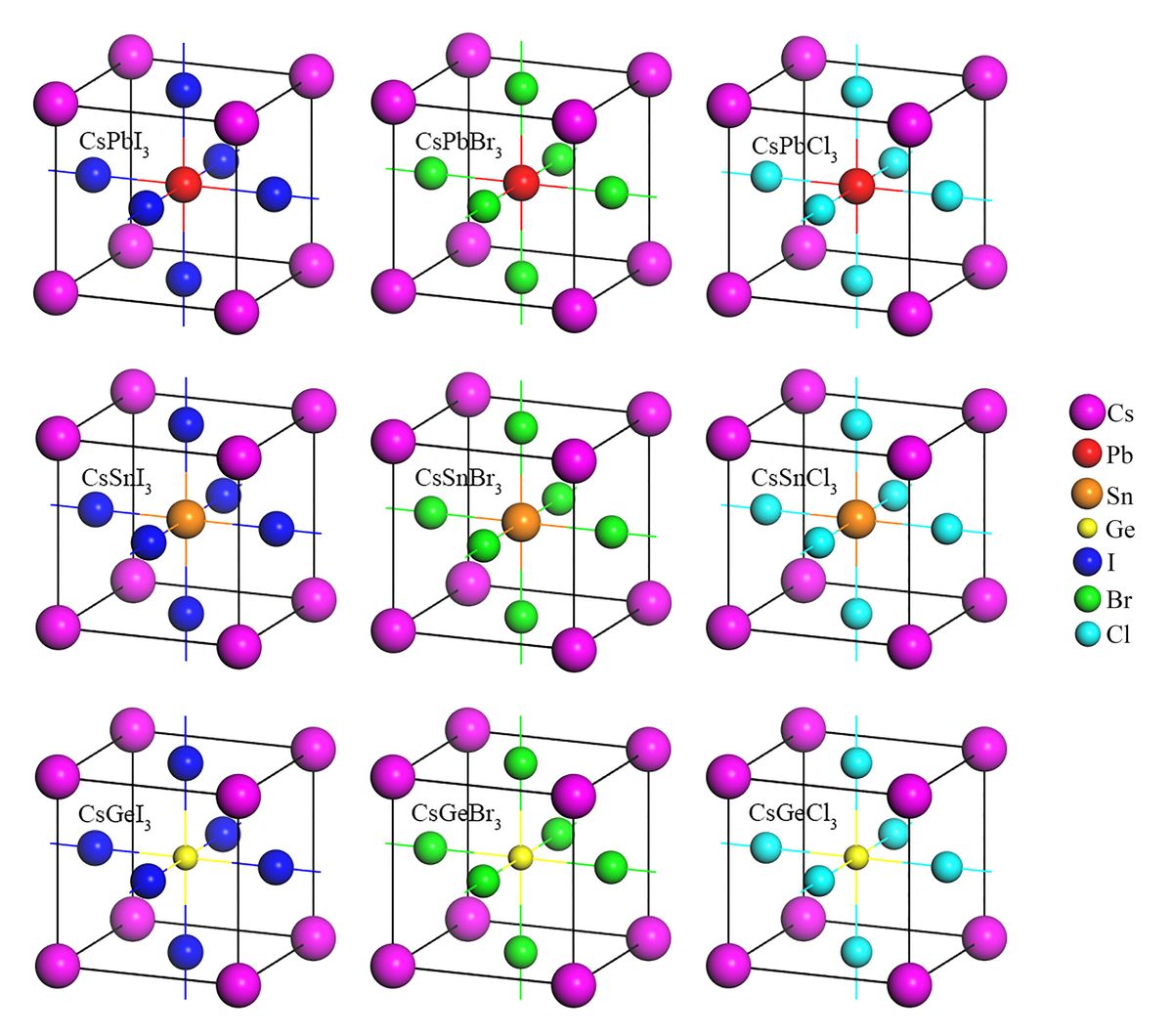
Inorganic Halide Perovskites for Photovoltaics and Optoelectronics
Lead (Pb) free non-toxic perovskite solar cells have become more important in the commercialization of the photovoltaic devices. In this study the structural, electronic, optical and mechanical properties of Pb-free inorganic metal halide cubic perovskites CsBX3 (B = Sn, Ge; X = I, Br, Cl) for perovskite solar cells are simulated using first-principles Density Functional Theory (DFT). These compounds are semiconductors with direct band gap energy and mechanically stable. Results suggest that the materials have high absorption coefficient, low reflectivity and high optical conductivity with potential application in solar cells and other optoelectronic energy devices. On the basis of the optical properties, one can expect that the Germanium (Ge) would be a better replacement of Pb as Ge containing compounds have higher optical absorption and optical conductivity than that of Pb containing compounds. A combinational analysis of the electronic, optical and mechanical properties of the compounds suggests that CsGeI3 based perovskite is the best Pb-free inorganic metal halide semiconductor for the solar cell application. However, the compound with solid solution of CsGe(I0.7Br0.3)3 is found to be mechanically more ductile than CsGeI3. This study will also guide to obtain Pb-free organic perovskites for optoelectronic devices.
More details can be found in the following published article:
Towards lead-free perovskite photovoltaics and optoelectronics by ab-initio simulations

