Formamidinium Based Hybrid Perovskites for Photovoltaics and Optoelectronics
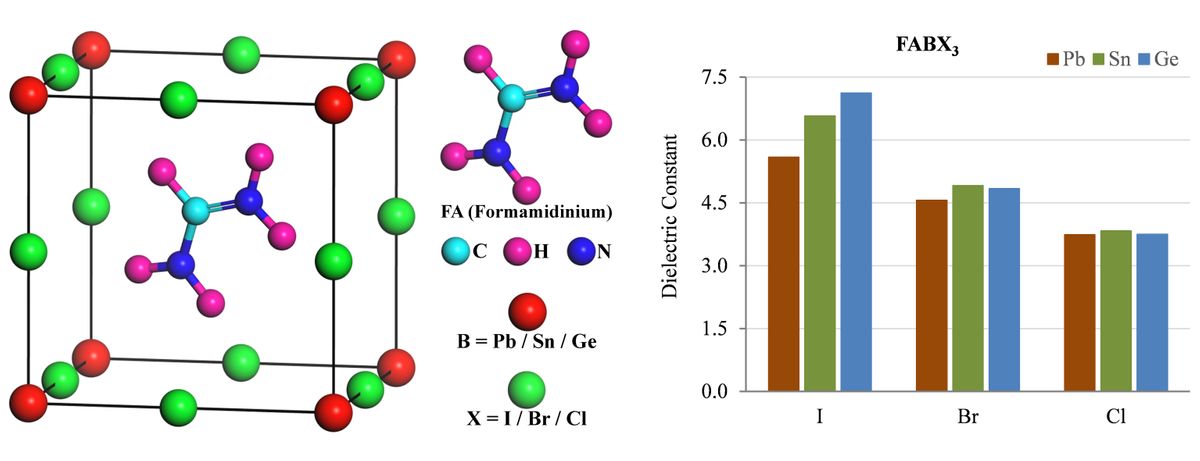
Lead (Pb) free non-toxic halide perovskites have drawn significant interest because of their promising optoelectronic properties and wide range of potential applications. Here we report the structural, electronic, optical and elastic properties of formamidinium (FA) based Pb-free non-toxic halide hybrid perovskites FABX3 [FA = CH(NH2)2; B = Sn, Ge; X = I, Br, Cl]. These properties are compared with its Pb-based counterparts FAPbX3 (X = I, Br, Cl). Our first-principles density functional theory (DFT) investigations reveal that the selected materials are semiconductors having direct band gap. The results reveal that the studied compounds have low carrier effective masses, high absorption coefficients and high optical conductivities that make the materials promising for a vast range of optoelectronic applications. Our study also indicates that both the tin (Sn) and germanium (Ge) containing iodides have superior optoelectronic properties over the considered Pb-free bromides and chlorides. In addition, the Sn-containing iodide (FASnI3) shows better flexibility than its Ge-containing counterpart in terms of the investigated mechanical properties. More specifically, the perovskite FASnI3 would be the preferred Pb-free material for photovoltaic applications because of its low carrier effective mass and high absorption coefficient as well as the good material ductility. These results can help understanding the structure-property relationships of hybrid perovskites for the development of non-toxic sustainable optoelectronic devices.
More details can be found in the following published article:

